Introduction:
In the world of pharmaceuticals and food production, ensuring quality and safety is paramount. To achieve this, regulatory bodies have established Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) standards, which set the guidelines for the design, operation, and monitoring of utilities in these industries.

Utilities include: but are not limited to, electrical power; compressed air ; heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems: steam; gases, including medicinal; water, including potable and water for injection (WF); vacuum; and drains.
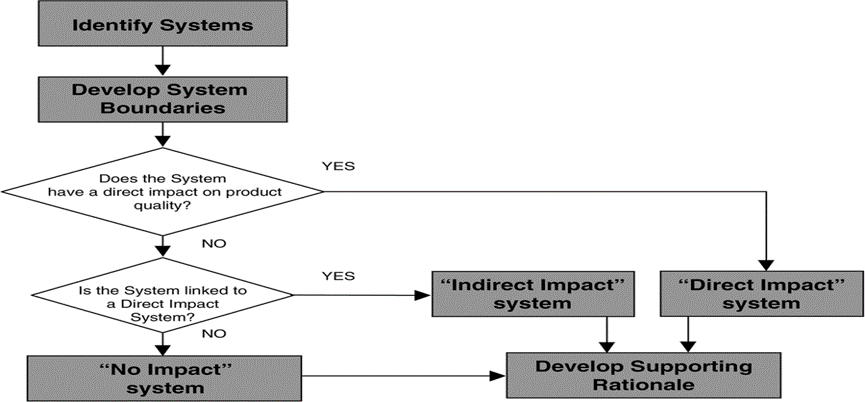
Direct Impact Utilities:
In the realm of GMP standards, utilities such as water, gases, and steam play a crucial role in ensuring product quality. The direct Impact utilities are those that:
1) has direct contact with the product
(e.g., HVAC System)
2) Provides an excipient, or produces an ingredient or solvent
(e.g., Purified Water and water for injection)
3) Is used in cleaning or sterilizing
(e.g., Clean Steam)
4) Preserves product status
(e.g., Gases- Nitrogen)
This emphasizes the need for rigorous control over GMP utilities such as HVAC System, water Stations, gases, and steam for sterilization. (ISPE-Baseline 5- Commissioning& Qualification)
Design, Installation, and Qualification:
Once utilities have been designed and installed, qualification/ validation should be done to ensure the system is capable.
Operation:
Utilities should undergo routine calibration, inspection, and checks to ensure proper performance. Written records of these checks and inspections must be maintained to demonstrate compliance.
Quality testing methods:
l along with acceptable thresholds, should be developed and documented in appropriate procedures and work instructions. These procedures should document :
– who will conduct the sampling,
– when samples will be taken
– the minimum required sample volume,
– handling and storage of samples
– chemical, biological, and particulate levels,
– and how to handle out of specification (OOS)
Ongoing Monitoring and Validation:
GMP standards emphasize that qualification and validation should not be one-off exercises. An ongoing program should follow their initial implementation and should be based on an annual review. This ensures that systems and processes are continually evaluated to verify their valid operation, with revalidation being necessary only when significant changes occur.
Conclusion:
Adhering to GMP standards is non-negotiable in the pharmaceutical and food Utilities, such as water, gases, and steam, are essential components that directly impact product quality. Understanding the intricacies of GMP standards, including the design, operation, and monitoring of utilities, is crucial to maintaining product quality and safety. staying committed to these standards is to ensure that products meet the highest quality and safety benchmarks.
References
1. Volume 4 EU , Annex 1 Manufacture of Sterile Medicinal Products
2. Volume 4 EU , Annex 15 Qualification and Validation
3. WHO Technical Report Series, No. 986, 2011, ,Annex 2, WHO good manufacturing practices for pharmaceutical products: main principles
4. ISPE -Baseline 5- Commissioning& Qualification